Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) (ULTIMATE)
Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 10.4.
NOTE: 4 of the top 6 attacks were application based. Download our whitepaper, "A Seismic Shift in Application Security" to learn how to protect your organization.
Running static checks on your code is the first step to detect vulnerabilities that can put the security of your code at risk. Yet, once deployed, your application is exposed to a new category of possible attacks, such as cross-site scripting or broken authentication flaws. This is where Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) comes into place.
Overview
If you're using GitLab CI/CD, you can analyze your running web applications
for known vulnerabilities using Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST).
You can take advantage of DAST by either including the CI job in
your existing .gitlab-ci.yml file or by implicitly using
Auto DAST,
provided by Auto DevOps.
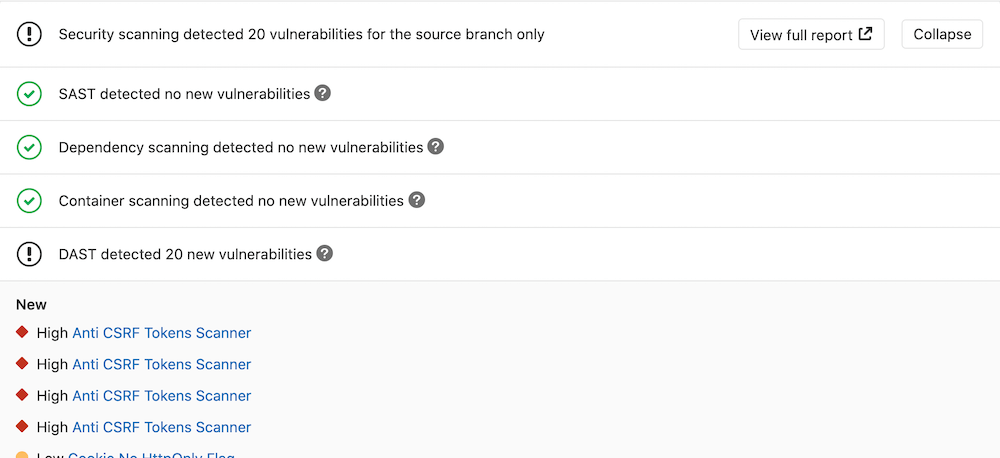
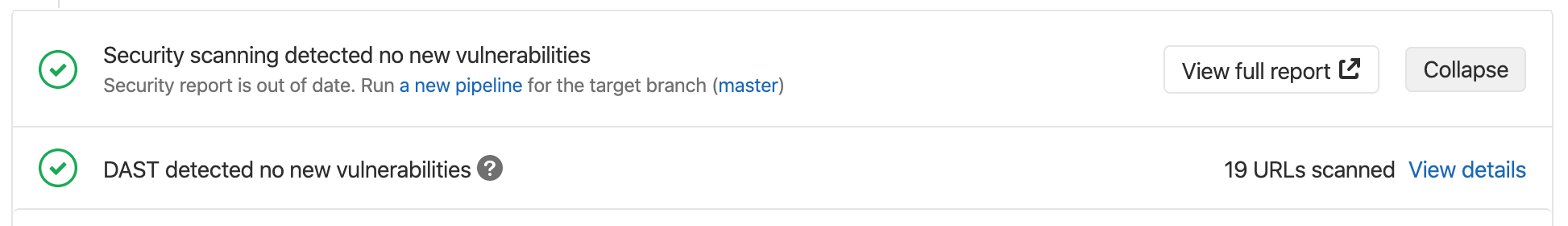
GitLab checks the DAST report, compares the found vulnerabilities between the source and target branches, and shows the information on the merge request.
NOTE: Note: This comparison logic uses only the latest pipeline executed for the target branch's base commit. Running the pipeline on any other commit has no effect on the merge request.
By clicking on one of the detected linked vulnerabilities, you can see the details and the URL(s) affected.
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) uses the popular open source tool OWASP ZAProxy to perform an analysis on your running web application.
By default, DAST executes ZAP Baseline Scan and performs passive scanning only. It won't actively attack your application. However, DAST can be configured to also perform an active scan: attack your application and produce a more extensive security report. It can be very useful combined with Review Apps.
NOTE: Note: A pipeline may consist of multiple jobs, including SAST and DAST scanning. If any job fails to finish for any reason, the security dashboard won't show DAST scanner output. For example, if the DAST job finishes but the SAST job fails, the security dashboard won't show DAST results. The analyzer will output an exit code on failure.
Use cases
It helps you automatically find security vulnerabilities in your running web applications while you're developing and testing your applications.
Requirements
To run a DAST job, you need GitLab Runner with the
docker executor.
Configuration
For GitLab 11.9 and later, to enable DAST, you must
include the
DAST.gitlab-ci.yml template
that's provided as a part of your GitLab installation. For GitLab versions earlier
than 11.9, you can copy and use the job as defined in that template.
Add the following to your .gitlab-ci.yml file:
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
DAST_WEBSITE: https://example.comThere are two ways to define the URL to be scanned by DAST:
-
Set the
DAST_WEBSITEvariable. -
Add it in an
environment_url.txtfile at the root of your project. This is great for testing in dynamic environments. In order to run DAST against an app dynamically created during a GitLab CI/CD pipeline, have the app persist its domain in anenvironment_url.txtfile, and DAST automatically parses that file to find its scan target. You can see an example of this in our Auto DevOps CI YAML.
If both values are set, the DAST_WEBSITE value takes precedence.
The included template creates a dast job in your CI/CD pipeline and scans
your project's source code for possible vulnerabilities.
The results are saved as a DAST report artifact that you can later download and analyze. Due to implementation limitations we always take the latest DAST artifact available. Behind the scenes, the GitLab DAST Docker image is used to run the tests on the specified URL and scan it for possible vulnerabilities.
By default, the DAST template will use the latest major version of the DAST Docker
image. Using the DAST_VERSION variable, you can choose how DAST updates:
- Automatically update DAST with new features and fixes by pinning to a major version (such as
1). - Only update fixes by pinning to a minor version (such as
1.6). - Prevent all updates by pinning to a specific version (such as
1.6.4).
Find the latest DAST versions on the Releases page.
When DAST scans run
When using DAST.gitlab-ci.yml template, the dast job is run last as shown in
the example below. To ensure DAST is scanning the latest code, your CI pipeline
should deploy changes to the web server in one of the jobs preceding the dast job.
stages:
- build
- test
- deploy
- dastBe aware that if your pipeline is configured to deploy to the same webserver in each run, running a pipeline while another is still running could cause a race condition where one pipeline overwrites the code from another pipeline. The site to be scanned should be excluded from changes for the duration of a DAST scan. The only changes to the site should be from the DAST scanner. Be aware that any changes that users, scheduled tasks, database changes, code changes, other pipelines, or other scanners make to the site during a scan could lead to inaccurate results.
Authentication
It's also possible to authenticate the user before performing the DAST checks:
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
DAST_WEBSITE: https://example.com
DAST_AUTH_URL: https://example.com/sign-in
DAST_USERNAME: john.doe@example.com
DAST_PASSWORD: john-doe-password
DAST_USERNAME_FIELD: session[user] # the name of username field at the sign-in HTML form
DAST_PASSWORD_FIELD: session[password] # the name of password field at the sign-in HTML form
DAST_AUTH_EXCLUDE_URLS: http://example.com/sign-out,http://example.com/sign-out-2 # optional, URLs to skip during the authenticated scan; comma-separated, no spaces in betweenThe results will be saved as a DAST report artifact that you can later download and analyze. Due to implementation limitations, we always take the latest DAST artifact available.
DANGER: Danger: NEVER run an authenticated scan against a production server. When an authenticated scan is run, it may perform any function that the authenticated user can. This includes actions like modifying and deleting data, submitting forms, and following links. Only run an authenticated scan against a test server.
Full scan
DAST can be configured to perform ZAP Full Scan, which includes both passive and active scanning against the same target website:
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
DAST_FULL_SCAN_ENABLED: "true"Domain validation
The DAST job can be run anywhere, which means you can accidentally hit live web servers and potentially damage them. You could even take down your production environment. For that reason, you should use domain validation.
Domain validation is not required by default. It can be required by setting the
environment variable DAST_FULL_SCAN_DOMAIN_VALIDATION_REQUIRED to "true".
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
DAST_FULL_SCAN_ENABLED: "true"
DAST_FULL_SCAN_DOMAIN_VALIDATION_REQUIRED: "true"Since ZAP full scan actively attacks the target application, DAST sends a ping
to the target (normally defined in DAST_WEBSITE or environment_url.txt) beforehand.
- If
DAST_FULL_SCAN_DOMAIN_VALIDATION_REQUIREDisfalseor unset, the scan will proceed unless the response to the ping includes aGitlab-DAST-Permissionheader with a value ofdeny. - If
DAST_FULL_SCAN_DOMAIN_VALIDATION_REQUIREDistrue, the scan will exit unless the response to the ping includes aGitlab-DAST-Permissionheader with a value ofallow.
Here are some examples of adding the Gitlab-DAST-Permission header to a response
in Rails, Django, and Node (with Express).
Ruby on Rails
Here's how you would add a custom header in Ruby on Rails:
class DastWebsiteTargetController < ActionController::Base
def dast_website_target
response.headers['Gitlab-DAST-Permission'] = 'allow'
head :ok
end
endDjango
Here's how you would add a custom header in Django:
class DastWebsiteTargetView(View):
def head(self, *args, **kwargs):
response = HttpResponse()
response['Gitlab-Dast-Permission'] = 'allow'
return responseNode (with Express)
Here's how you would add a custom header in Node (with Express):
app.get('/dast-website-target', function(req, res) {
res.append('Gitlab-DAST-Permission', 'allow')
res.send('Respond to DAST ping')
})Domain validation header via a proxy
It's also possible to add the Gitlab-DAST-Permission header via a proxy.
NGINX
The following configuration allows NGINX to act as a reverse proxy and add the
Gitlab-DAST-Permission header:
# default.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
proxy_pass http://test-application;
add_header Gitlab-DAST-Permission allow;
}
}Apache
Apache can also be used as a reverse proxy
to add the Gitlab-DAST-Permission header.
To do so, add the following lines to httpd.conf:
# httpd.conf
LoadModule proxy_module modules/mod_proxy.so
LoadModule proxy_connect_module modules/mod_proxy_connect.so
LoadModule proxy_http_module modules/mod_proxy_http.so
<VirtualHost *:80>
ProxyPass "/" "http://test-application.com/"
ProxyPassReverse "/" "http://test-application.com/"
Header set Gitlab-DAST-Permission "allow"
</VirtualHost>This snippet contains a complete httpd.conf file
configured to act as a remote proxy and add the Gitlab-DAST-Permission header.
API scan
Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 12.10.
Using an API specification as a scan's target is a useful way to seed URLs for scanning an API. Vulnerability rules in an API scan are different than those in a normal website scan.
Specification format
API scans support OpenAPI V2 and OpenAPI V3 specifications. You can define these specifications using JSON or YAML.
Import API specification from a URL
If your API specification is accessible at a URL, you can pass that URL in directly as the target. The specification does not have to be hosted on the same host as the API being tested.
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
DAST_API_SPECIFICATION: http://my.api/api-specification.ymlImport API specification from a file
If your API specification is in your repository, you can provide the specification's
filename directly as the target. The specification file is expected to be in the
/zap/wrk directory.
dast:
script:
- mkdir -p /zap/wrk
- cp api-specification.yml /zap/wrk/api-specification.yml
- /analyze -t $DAST_WEBSITE
variables:
GIT_STRATEGY: fetch
DAST_API_SPECIFICATION: api-specification.ymlFull scan
API scans support full scanning, which can be enabled by using the DAST_FULL_SCAN_ENABLED
environment variable. Domain validation is not supported for full API scans.
Host override
Specifications often define a host, which contains a domain name and a port. The
host referenced may be different than the host of the API's review instance.
This can cause incorrect URLs to be imported, or a scan on an incorrect host.
Use the DAST_API_HOST_OVERRIDE environment variable to override these values.
For example, with a OpenAPI V3 specification containing:
servers:
- url: https://api.host.comIf the test version of the API is running at https://api-test.host.com, then
the following DAST configuration can be used:
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
DAST_API_SPECIFICATION: http://api-test.host.com/api-specification.yml
DAST_API_HOST_OVERRIDE: api-test.host.comNote that DAST_API_HOST_OVERRIDE is only applied to specifications imported by URL.
Authentication using headers
Tokens in request headers are often used as a way to authenticate API requests.
You can achieve this by using the DAST_REQUEST_HEADERS environment variable.
Headers are applied to every request DAST makes.
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
DAST_API_SPECIFICATION: http://api-test.api.com/api-specification.yml
DAST_REQUEST_HEADERS: "Authorization: Bearer my.token"Customizing the DAST settings
The DAST settings can be changed through environment variables by using the
variables parameter in .gitlab-ci.yml.
These variables are documented in available variables.
For example:
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
variables:
DAST_WEBSITE: https://example.com
DAST_TARGET_AVAILABILITY_TIMEOUT: 120Because the template is evaluated before the pipeline configuration, the last mention of the variable will take precedence.
Overriding the DAST template
CAUTION: Deprecation:
Beginning in GitLab 13.0, the use of only and except
is no longer supported. When overriding the template, you must use rules instead.
If you want to override the job definition (for example, change properties like
variables or dependencies), you need to declare a dast job after the
template inclusion and specify any additional keys under it. For example:
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
dast:
stage: dast # IMPORTANT: don't forget to add this
variables:
DAST_WEBSITE: https://example.com
CI_DEBUG_TRACE: "true"As the DAST job belongs to a separate dast stage that runs after all
default stages,
don't forget to add stage: dast when you override the template job definition.
Available variables
DAST can be configured using environment variables.
| Environment variable | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|
SECURE_ANALYZERS_PREFIX |
no | Set the Docker registry base address from which to download the analyzer. |
DAST_WEBSITE |
no | The URL of the website to scan. DAST_API_SPECIFICATION must be specified if this is omitted. |
DAST_API_SPECIFICATION |
no | The API specification to import. DAST_WEBSITE must be specified if this is omitted. |
DAST_AUTH_URL |
no | The authentication URL of the website to scan. Not supported for API scans. |
DAST_USERNAME |
no | The username to authenticate to in the website. |
DAST_PASSWORD |
no | The password to authenticate to in the website. |
DAST_USERNAME_FIELD |
no | The name of username field at the sign-in HTML form. |
DAST_PASSWORD_FIELD |
no | The name of password field at the sign-in HTML form. |
DAST_AUTH_EXCLUDE_URLS |
no | The URLs to skip during the authenticated scan; comma-separated, no spaces in between. Not supported for API scans. |
DAST_TARGET_AVAILABILITY_TIMEOUT |
no | Time limit in seconds to wait for target availability. Scan is attempted nevertheless if it runs out. Integer. Defaults to 60. |
DAST_FULL_SCAN_ENABLED |
no | Switches the tool to execute ZAP Full Scan instead of ZAP Baseline Scan. Boolean. true, True, or 1 are considered as true value, otherwise false. Defaults to false. |
DAST_FULL_SCAN_DOMAIN_VALIDATION_REQUIRED |
no | Requires domain validation when running DAST full scans. Boolean. true, True, or 1 are considered as true value, otherwise false. Defaults to false. Not supported for API scans. |
DAST_AUTO_UPDATE_ADDONS |
no | By default the versions of ZAP add-ons are pinned to those provided with the DAST image. Set to true to allow ZAP to download the latest versions. |
DAST_API_HOST_OVERRIDE |
no | Used to override domains defined in API specification files. |
DAST_EXCLUDE_RULES |
no | Set to a comma-separated list of Vulnerability Rule IDs to exclude them from the scan report. Currently, excluded rules will get executed but the alerts from them will be suppressed. Rule IDs are numbers and can be found from the DAST log or on the ZAP project. For example, HTTP Parameter Override has a rule ID of 10026. |
DAST_REQUEST_HEADERS |
no | Set to a comma-separated list of request header names and values. For example, Cache-control: no-cache,User-Agent: DAST/1.0
|
DAST_ZAP_USE_AJAX_SPIDER |
no | Use the AJAX spider in addition to the traditional spider, useful for crawling sites that require JavaScript. Boolean. true, True, or 1 are considered as true value, otherwise false. Defaults to false. |
DAST command-line options
Not all DAST configuration is available via environment variables. To find out all possible options, run the following configuration. Available command-line options will be printed to the job log:
include:
template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
dast:
script:
- /analyze --helpYou must then overwrite the script command to pass in the appropriate argument.
For example, debug messages can be enabled by using -d, as shown in the following configuration:
include:
template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
dast:
script:
- export DAST_WEBSITE=${DAST_WEBSITE:-$(cat environment_url.txt)}
- /analyze -d -t $DAST_WEBSITECustom ZAProxy configuration
The ZAProxy server contains many useful configurable values.
Many key/values for -config remain undocumented, but there is an untested list of
possible keys.
Note that these options are not supported by DAST, and may break the DAST scan
when used. An example of how to rewrite the Authorization header value with TOKEN follows:
include:
template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
dast:
script:
- export DAST_WEBSITE=${DAST_WEBSITE:-$(cat environment_url.txt)}
- /analyze -z"-config replacer.full_list\(0\).description=auth -config replacer.full_list\(0\).enabled=true -config replacer.full_list\(0\).matchtype=REQ_HEADER -config replacer.full_list\(0\).matchstr=Authorization -config replacer.full_list\(0\).regex=false -config replacer.full_list\(0\).replacement=TOKEN" -t $DAST_WEBSITECloning the project's repository
The DAST job does not require the project's repository to be present when running, so by default
GIT_STRATEGY is set to none.
Running DAST in an offline environment
For self-managed GitLab instances in an environment with limited, restricted, or intermittent access to external resources through the internet, some adjustments are required for the DAST job to successfully run. For more information, see Offline environments.
Requirements for offline DAST support
To use DAST in an offline environment, you need:
- GitLab Runner with the
dockerorkubernetesexecutor. - Docker Container Registry with a locally available copy of the DAST container image, found in the DAST container registry.
NOTE: Note:
GitLab Runner has a default pull policy of always,
meaning the Runner tries to pull Docker images from the GitLab container registry even if a local
copy is available. GitLab Runner's pull_policy can be set to if-not-present
in an offline environment if you prefer using only locally available Docker images. However, we
recommend keeping the pull policy setting to always if not in an offline environment, as this
enables the use of updated scanners in your CI/CD pipelines.
Make GitLab DAST analyzer images available inside your Docker registry
For DAST, import the following default DAST analyzer image from registry.gitlab.com to your local Docker container registry:
registry.gitlab.com/gitlab-org/security-products/dast:latest
The process for importing Docker images into a local offline Docker registry depends on your network security policy. Please consult your IT staff to find an accepted and approved process by which external resources can be imported or temporarily accessed. Note that these scanners are updated periodically with new definitions, so consider if you're able to make periodic updates yourself.
For details on saving and transporting Docker images as a file, see Docker's documentation on
docker save,
docker load,
docker export, and
docker import.
Set DAST CI job variables to use local DAST analyzers
Add the following configuration to your .gitlab-ci.yml file. You must replace image to refer to
the DAST Docker image hosted on your local Docker container registry:
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
dast:
image: registry.example.com/namespace/dast:latestThe DAST job should now use local copies of the DAST analyzers to scan your code and generate security reports without requiring internet access.
Alternatively, you can use the variable SECURE_ANALYZERS_PREFIX to override the base registry address of the dast image.
Reports
The DAST job can emit various reports.
List of URLs scanned
When DAST completes scanning, the merge request page states the number of URLs scanned. Click View details to view the web console output which includes the list of scanned URLs.
JSON
CAUTION: Caution: The JSON report artifacts are not a public API of DAST and their format is expected to change in the future.
The DAST tool always emits a JSON report file called gl-dast-report.json and
sample reports can be found in the
DAST repository.
There are two formats of data in the JSON report that are used side by side:
- The proprietary ZAP format that will be eventually deprecated.
- A common format that will be the default in the future.
Other formats
Reports can also be generated in Markdown, HTML, and XML.
Reports can be published as artifacts using the following configuration:
include:
template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
dast:
script:
- export DAST_WEBSITE=${DAST_WEBSITE:-$(cat environment_url.txt)}
- /analyze -r report.html -w report.md -x report.xml -t $DAST_WEBSITE
- cp /zap/wrk/report.{html,md,xml} "$PWD"
artifacts:
paths:
- report.html
- report.md
- report.xml
- gl-dast-report.jsonSecurity Dashboard
The Security Dashboard is a good place to get an overview of all the security vulnerabilities in your groups, projects and pipelines. Read more about the Security Dashboard.
Bleeding-edge vulnerability definitions
ZAProxy first creates rules in the alpha class. After a testing period with the
community, they are promoted to beta. DAST uses beta definitions by default.
To request alpha definitions, use -a as shown in the following configuration:
include:
template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
dast:
script:
- export DAST_WEBSITE=${DAST_WEBSITE:-$(cat environment_url.txt)}
- /analyze -a -t $DAST_WEBSITEInteracting with the vulnerabilities
Once a vulnerability is found, you can interact with it. Read more on how to interact with the vulnerabilities.
Vulnerabilities database update
For more information about the vulnerabilities database update, check the maintenance table.
Optimizing DAST
By default, DAST will download all artifacts defined by previous jobs in the pipeline. If
your DAST job does not rely on environment_url.txt to define the URL under test or any other files created
in previous jobs, we recommend you don't download artifacts. To avoid downloading
artifacts, add the following to your gitlab-ci.yml file:
dast:
dependencies: []Troubleshooting
Running out of memory
By default, ZAProxy, which DAST relies on, is allocated memory that sums to 25% of the total memory on the host. Since it keeps most of its information in memory during a scan, it's possible for DAST to run out of memory while scanning large applications. This results in the following error:
[zap.out] java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap spaceFortunately, it's straightforward to increase the amount of memory available
for DAST by overwriting the script key in the DAST template:
include:
- template: DAST.gitlab-ci.yml
dast:
script:
- export DAST_WEBSITE=${DAST_WEBSITE:-$(cat environment_url.txt)}
- /analyze -t $DAST_WEBSITE -z"-Xmx3072m"Here, DAST is being allocated 3072 MB.
Change the number after -Xmx to the required memory amount.