Kubernetes Logs
- Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 11.0.
- Moved to GitLab Core 12.9.
GitLab makes it easy to view the logs of running pods in connected Kubernetes clusters. By displaying the logs directly in GitLab in the Log Explorer, developers can avoid managing console tools or jumping to a different interface.
NOTE: Kubernetes + GitLab Everything you need to build, test, deploy, and run your application at scale. Learn more.
Overview
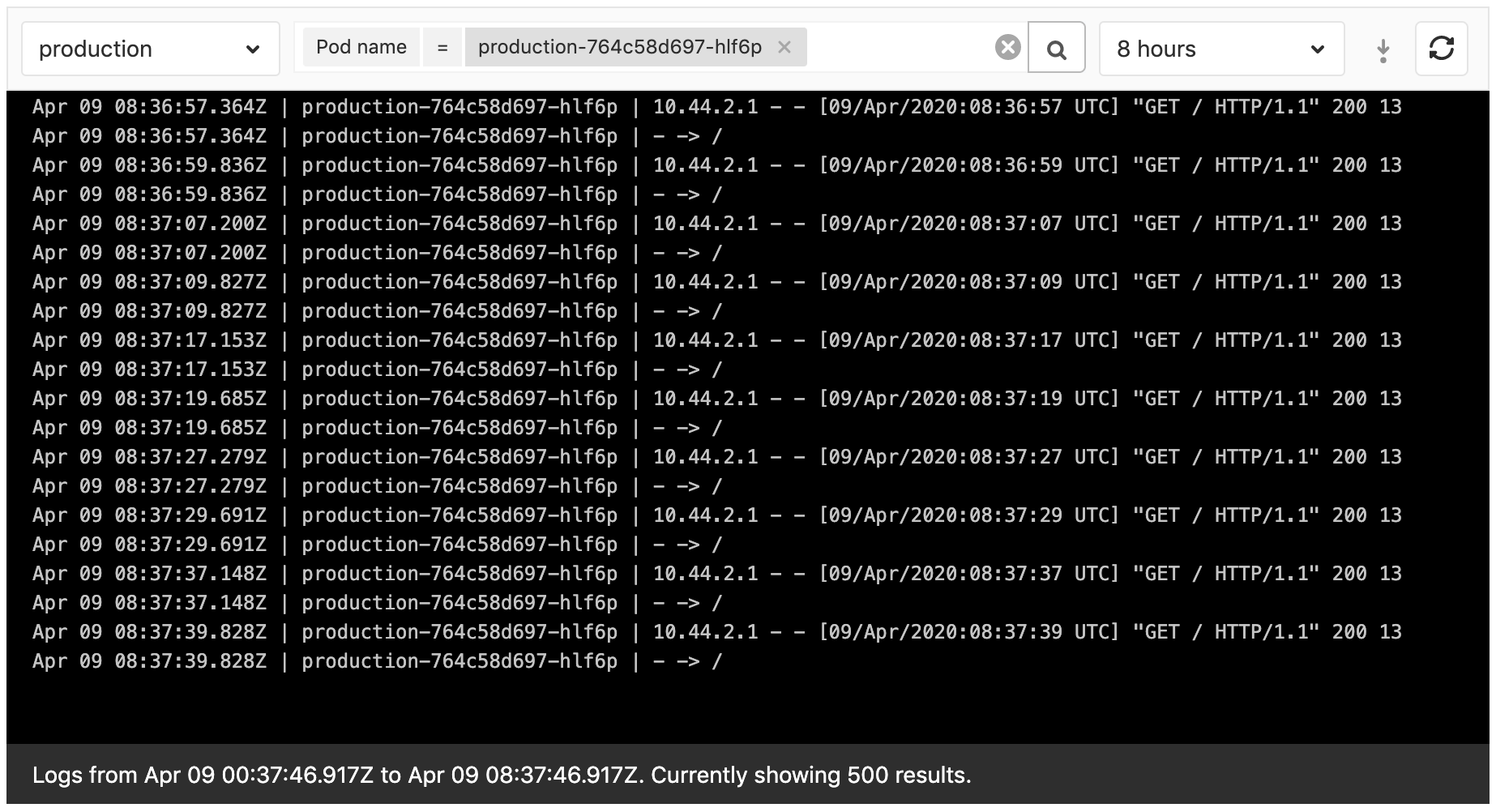
Kubernetes logs can be viewed directly within GitLab with the Log Explorer.
To learn more, see APM - Log Explorer.
Requirements
Deploying to a Kubernetes environment is required to use Logs.
Usage
To access logs, you must have the right permissions.
You can access them in two ways.
From the project sidebar
Introduced in GitLab 12.5.
Go to {cloud-gear} Operations > Pod logs on the sidebar menu to display the Log Explorer.
From Deploy Boards
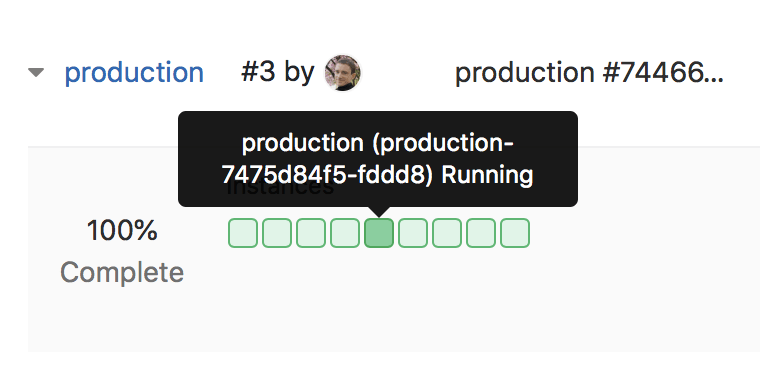
Logs can be displayed by clicking on a specific pod from Deploy Boards:
- Go to {cloud-gear} Operations > Environments and find the environment
which contains the desired pod, like
production. - On the Environments page, you should see the status of the environment's pods with Deploy Boards.
- When mousing over the list of pods, a tooltip will appear with the exact pod name
and status.

- Click on the desired pod to display the Log Explorer.
Logs view
The Log Explorer lets you filter the logs by:
- Pods.
- From GitLab 12.4, environments.
- From GitLab 12.7, full text search.
- From GitLab 12.8, dates.
Loading more than 500 log lines is possible from GitLab 12.9 onward.
Support for pods with multiple containers is coming in a future release.
Support for historical data is coming in a future release.
Filter by date
Introduced in GitLab 12.8.
When you enable Elastic Stack on your cluster, you can filter logs displayed in the Log Explorer by date.
Click Show last in the Log Explorer to see the available options.
Full text search
Introduced in GitLab 12.7.
When you enable Elastic Stack on your cluster, you can search the content of your logs through a search bar.
The search is passed on to Elasticsearch using the simple_query_string Elasticsearch function, which supports the following operators:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| |
An OR operation. |
- |
Negates a single token. |
+ |
An AND operation. |
" |
Wraps a number of tokens to signify a phrase for searching. |
* (at the end of a term) |
A prefix query. |
( and )
|
Precedence. |
~N (after a word) |
Edit distance (fuzziness). |
~N (after a phrase) |
Slop amount. |